PowerGramo Offline Recorder is an easy-to-use audio recorder you
can use to record all kinds of sound on your computer into
MP3 / WMA / OGG / WAV files with high quality.
It's able to record audio from microphones, line-in, phone
line, cassette tape, video tape and more other input devices.
The audio recorder also supports recording from other windows
applications, like winamp, media player, etc. This makes it
very easy to record online radio, broadcast and other internet
sound. It simply makes a complete audio recording studio of
your computer!
1. Understand some basic concept of sound recording.
2. Configurations before recording.
2.1 Select an audio
device.
2.2 Select output format.
2.3 Select an audio
line according your recording task.
2.4 Select encoding
method.
2.5 Select a folder
for saving records.
3. Operations
3.1 Recording.
3.2 Playing during
pause of recording.
3.3 Saving recorded
data.
3.4 Manage records.
4. Understand mixer and record audio line (inside
learning).
1. Understand some basic
concept of sound recording.
Record sound on a PC is through a sound card, convert analog
signal to digital. it controlled by the following parameters:
• Bit
rate:
Bit rate (or bit depth) describes how many binary digits a
digital audio file uses to describe the amplitude of the audio
it is recreating. Each bit doubles the accuracy with which
an amplitude level can be described (16 bit = 65,536 possible
levels). Record on a PC , it can be 16 bit or 8 bit. Obviously
using 16 bit will create higher quality sound but need more
storage.
• Sampling
rate (frequency):
Sampling rate is the number of values (samples) measured per
second in the conversion of audio from analog to digital.
The standard CD digital rate of 44.1 KHz restricts the maximum
sampled frequency to 22.05KHz. For a point of comparison,
Human hearing is usually said to be 20Hz to 20KHz. PowerGramo
Offline Recorder support following frequencies: 8000, 11025,
16000, 22050, 32000, 44100, 48000. The higher the frequency,
a higher sound quality can be produced.
• Channel number:
It can be either stereo or mono. Stereophonic sound, commonly
called stereo, is the reproduction of sound, using two independent
audio channels, through a pair of widely separated speaker
systems, in such a way as to create a pleasant and natural
impression of sound heard from various directions as in natural
hearing. Monaural (often shortened to mono) sound reproduction
is single-channel. Typically there is only one microphone,
one loudspeaker, or, in the case of headphones or multiple
loudspeakers, they are fed from a common signal path, and
in the case of multiple microphones, mixed into a signal path
at some stage.
2. Configurations before
recording.
2.1 Select an audio device.
All audio devices (sound cards) are listed in the device pull-down
list window. There you can select one of them. But usually
you have only one sound card installed on your computer.
2.2 Select output format.
Selecting output format means selecting the combination of
bit rate, channel number and sample rate (frequency). All
combinations PowerGramo Offline Recorder supports are listed in the
second pull down list window.
2.3 Select an audio line according
your recording task.
This is the most subtle configuring task. Which audio line
to be selected depends on what are you going to record.
• Record
Streaming Audio
A) Find audio line for streaming audio recording
Usually the audio line for streaming audio recording has the
name of Stereo Mix or Wave out .But its name may be different
for different sound card. If you know the name of stream audio
line, you just click on the checkbox shown at left side of
the name of the line.
B) Open other media player to play audio.
C) Click the record button to start recording, sound played
by the media player will be recorded.
• Record
from microphone
A) Connect microphone to your PC on jack of the sound
card.
B) Activate the audio line of microphone by checking the box
on the left-side of the line name.
C) Speak to microphone.
D) Click the record button to start recording.
• Record
from audio cassette player or DVD player
A) Connect audio cassette player or DVD player to your PC.
Use a single stereo audio cable to connect audio cassette
player to the line in jack of the sound card:
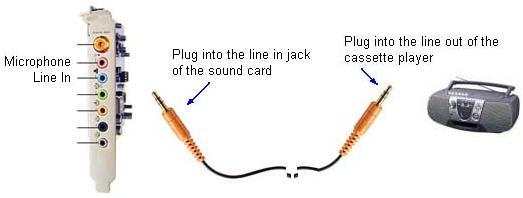
Use a stereo audio cable which one end has two single channel
plugs to connect audio cassette player to the line in jack
of the sound card:
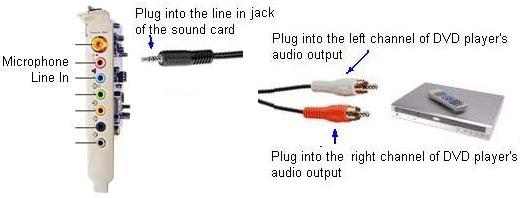
B) Select the audio line of Line In by click the check box
on left-side of it.
C) Play the audio cassette player or DVD player.
D) Click the record button to start recording.
2.4 Select encoding method.
Click button "Settings" to bring forth the Settings
window. There you can select one from the two encoding methods.
One is PCM encoding, which stores uncompressed raw audio data
(.wav files). Another is MPEG encoding that enables you to
compress audio data into MP3 files. But please note: if you
choose sample rate lower than 16000 or bit rate other than
16, even you select MPEG encoding method, audio data will
be saved in .wav files rather than in MP3 files.
2.5 Select a folder for saving records.
Click button "Settings". This will bring forth the
Settings window. The folder can be set there. If you didn't
set the folder or the folder you selected does not exist,
the program will prompt for saving location as you go to save
a record.
3. Operations.
3.1 Recording.
Press start button to start recording and press stop button
to stop recording. Be careful to note where the thumb of the
progress slider locates when you begin recording. The position
the thumb indicates is where new data will be written. So
data behind this position will be overwritten while recording
continues.
3.2 Playing during pause of recording.
When recording is paused, the play button is enabled. Then
you can press it to play sound that has been recorded. Press
stop button to stop playing.
3.3 Saving recorded data.
After recording, or when recording is paused, click save button
to save data. Depending on your settings, data maybe save
in raw format or compressed into mp3 format. After saving
a file, a new record will be added into the playlist.
You can also choose to pack audio data into a VEA file. To
do this, click "Save as VEA" button to save data.
VEA files enable you to save some comments together with the
audio data for further reference. For details about VEA file,
click
here.
3.4 Manage records.
All saved records will be displayed in the playlist window
at right side of the user interface. Beneath the playlist
window, buttons and a progress slider are provided for record
replaying. Clicking right mouse button in the playlist window
will bring forth a popup menu. By using it you can add audio
files into the list or remove items from the list.
4. Understand mixer and record audio
line(inside learning).
A sound card mixer is the part of a sound card that
can mix the sound input from different sources.
The following schematic shows how a sound card's mixer manipulates
sound from different sources:
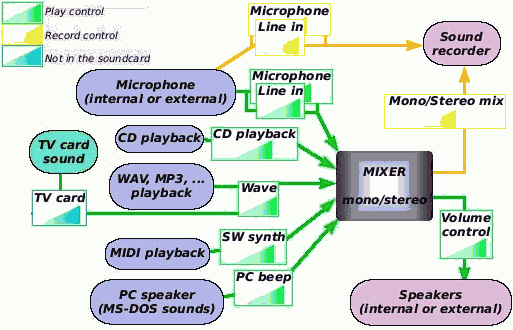
Play controls on a typical sound mixer:
| Control |
channels |
Controlled source |
| Wave* |
stereo |
Sound generated by the computer when playing MP3,
WAV,...
Also the sound when playing a CD-DA in some programs
(Windows Media Player, Media Player Classic) or playing
a MIDI in certain programs (JetAudio) |
| MIDI/SW Synth |
stereo |
Sound generated from a MIDI device or synthesizer
(electronic keyboard, Windows Media Player, IrfanView,
Media Player Classic, ...) |
| CD playback |
stereo |
Sound generated when playing a CD-DA in most programs
(JetAudio, IrfanView, ...) |
| Microphone |
mono |
Sound entering through an internal microphone, or
the microphone jack |
| Line in/Aux |
stereo |
Sound from an external source (iPod, television,
etc.) |
| SPDIF |
mono |
Uncommon digital interface of some devices |
| PC speaker |
mono |
Sound generated in the old internal PC speaker.
This is the sound heard in old MS-DOS programs and
on boot (on PC's) |
| Volume control |
stereo |
Mixed sound sent to the speakers (output) |
TV tuner cards and other similar devices output their sound
via the Wave channel.
Record controls:
| Control |
Channels |
Source |
| Stereo mix |
stereo |
Mixed sound sent to the recorder |
| Mono mix |
mono |
Mixed sound converted into mono, sent
to the recorder |
| Microphone |
mono |
Sound from the microphone that is directly
going to be recorded |
Record streaming sound
As this sound is controlled through wave control, you have
to set this volume in the playing control (maybe it's convenient
to mute all others, except volume control if you want to
hear it meanwhile). In recording, selecting stereo mix or
mono mix will enable you to record any other internal sound
of your PC, i.e. voices of TTS engines, sounds of the operating
system.



